International Trademark Registration

International Trademark Registration
What is International Trademark Registration?
International Trademarks are regulated by World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). WIPO is an agency established by United Nations (UN) in the year 1967 with an objective of protection of intellectual property throughout the world. International trademark registration and administration is regulated by a combination of WIPO treaties as well as other national and regional laws. Apart from national and regional laws following trademark related treaties regulate the legal framework of international trademarks.- Paris Convention adopted in 1883
- Madrid Agreement (Marks) concluded in 1891
- Madrid Protocol concluded in 1989
- NICE Agreement concluded in 1957 which established the NICE Classification
- Vienna Agreement it defied figurative elements of Marks
- Singapore Treaty of 1994
- Trademark Law Treaty
- Nairobi Treaty
Madrid System for International Trademark Registration
One can register an international trademark through Madrid System in multiple jurisdictions at the same time. This does not mean that it will be unified registration; it will create a bundle of national rights through one application which can be administered centrally. This is a simplified and convenient method through which one can file a single application and make payment of a single set of fees for registration, protection, and management of trademark in 117 countries which are members as contracting party. Starting from a start-up to a multinational organization, anyone can file for international trademark registration irrespective of the size of an organization.
Benefits of the Madrid System
-
Cost Effective
-
Convenience
-
Global Coverage
-
Efficient Brand Management
Who is eligible to use Madrid System?
Anyone who has any kind of personal or business connection with any of the member of the Madrid’s system is entitled to file an application for registration under this system. Now the question arises who are the members of the Madrid system. There are total 101 members of the System which covers 117 countries in total. These members are contracting parties of the above stated Madrid Agreement and Madrid Protocol. You can check the list of all the member of the Madrid System on the official website of WIPO.System of International Trademark Registration
The system of international trademark registration consists of three very important parts. Here we have listed out these three parts in precise-
Part I: Trademark Search
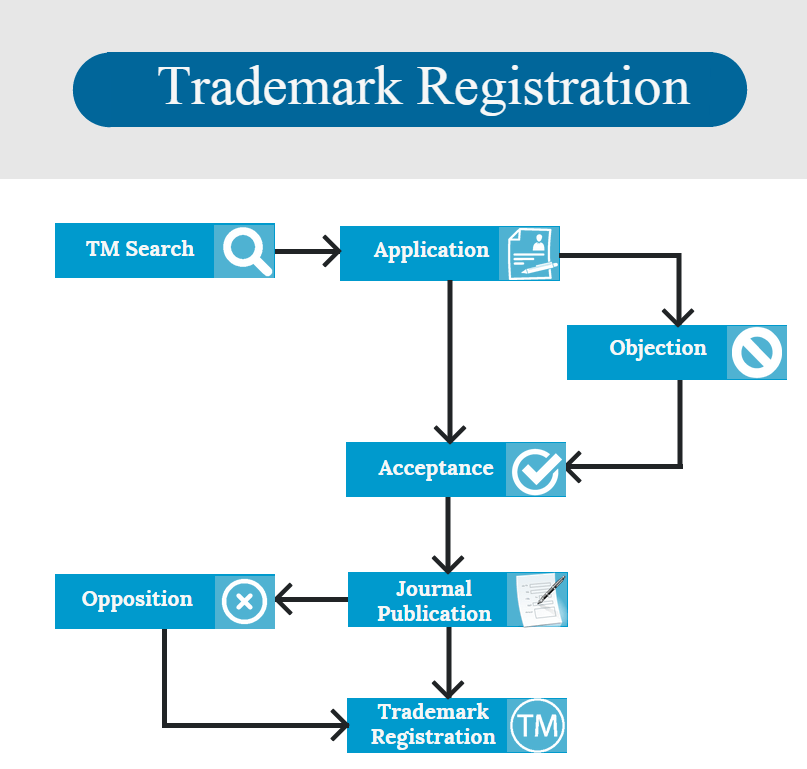
- Text used in the trademark
- Image used in the trademark
- Goods or Services class it is to be applied for
-
Part II: File Application for Registration
-
Part II: International Trademark Management
- Renewal of Trademark every 10 years
- E-payment of fees
- Expanding the geographical scope via filing in more countries
- Appointment of a new representative
- Transfer of Ownership
- Cancellation of trademark
Fees for international Trademark Registration
Under Madrid System the applicable fees for processing application for international trademark application constitute of three elements;- The basic application fees; this is for the mark to be registered
- A complementary feefor every contracting party (country) the application is made for i.e. the jurisdictions one wants to protect the mark in. In some cases, these complementary fees are individual fees.
- A supplementary feefor every class of goods or services trademark is applied for There might also be certain handling charges imposed by office of origin for verifying and forwarding the application to WIPO. In India, these handling charges are set at Rs. 2000.
Classification of Goods and Services under WIPO
As per the NICE Agreement executed at the Nice Diplomatic Conference conducted on June 15, 1957, an international standard of classification of goods and Services is established for the purpose of registration of marks. This standard of classification is known as Nice Classification also termed as NCL. This classification is based on classification prepared by BIRPI, the predecessor of WIPO in the year 1935. Initially, this classification consisted of 34 classes of goods and services. Over the years this list has been revised a few times. Its latest version of the eleventh edition was enforced on January 1, 2018. This latest version consists of total 45 classes (34 of goods and 11 of services). For the countries which are a part of NICE Agreement use of NICE Classification is mandatory not for national registration of marks as well as for international registrations.Pre-requisites for Registration
- If you are planning to file for international trademark registration it is a mandatory requirement that you have either already registered or have applied for same trademark in the Intellectual Property Office of the country of origine. the country from which the application will be filed from.
- The person planning to apply for international trademark registration must have either a personal or business connection with at least one of the contracting parties of the Madrid System. the country they have such connection with will be the place they will apply from i.e. office of origin. This connection can be defined in any of the following forms;
- The applicant is a domicile of the contracting party
- The applicant is a citizen of the contracting party
- The applicant has a business in the contracting party. Such business can either be real or effective industrial or commercial establishment.
Procedure of International Trademark Registration under Madrid System
-
First Step: Filing of Application
-
Second Step: Certification and Forwarded to WIPO
-
Third Step: Formal examination by WIPO
-
Fourth Step: Further examination by IP Office of Contracting Party
What We Offer
Packages & Pricing
6499
Basic
10000
Standard
19999
premium
FAQs For Private Limited Company Registration
LicenseHub - Copyright 2023. All rights reserved.
- Designed By-WebsApex


